Exploring DLT in Blockchain: The Ultimate Decentralization Breakdown
Have you found yourself asking, “What is DLT in blockchain and why does it matter?” You’re not alone. This digital ledger is more than tech talk; it’s a game-changer for how we will handle data and transactions for years to come. Let’s dive deep, shatter the jargon, and get to the core of how it offers rocks-solid security and transparency. I’ll guide you through the tangled webs of DLT, clearing out the fog around this tech gem, and why it’s set to rewrite the rules of business as we know it. Get ready for a thrilling journey into the heart of decentralized innovation, where every block and every chain matters.
Understanding the Basics of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Definition of Distributed Ledger Technology
What is DLT in blockchain? It’s a digital system for recording transactions. It spreads across many places at once. Unlike traditional databases, DLT has no central data store or admin function. This is DLT technology explained, in a nutshell.
Let’s dig in deeper. Imagine a notebook filled with details of who owns what. Now, picture countless copies of this notebook all over the world. Each copy gets updated with new info at the same time. This way, each page reflects the same transactions. That’s the essence of a distributed ledger.
How DLT Works and Its Core Functions
How does DLT work? Every node, or user, holds a copy of the ledger. When a transaction happens, every copy gets updated through a consensus mechanism. This ensures all copies match. Trust is not placed in a single entity but in the rules coded into the network. It’s about many agreeing on what’s true, not just one. This stops cheating since changing one copy is useless; every other copy would disagree.
Think of DLT as a team sport, where the game’s rules make sure every player agrees on the score. No one can change the score on their own. Everyone must play by the rules, or the game doesn’t work.
This technology powers lots of DLT platforms. It lets many people share access to the same data, at the same time. It’s perfect for business dealings, like tracking items in a supply chain.
DLT’s superpower is creating trust without needing a middleman. This is key in places like fintech, where money is online. It cuts out the need for a bank when two people want to pay each other.
Decentralization in DLT means no central point controls it. Everyone can see all transactions. This makes everything transparent. DLT and data integrity go hand in hand. Since all copies match, data can’t be changed without everyone knowing.
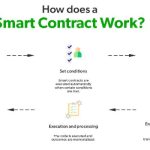
Smart contracts in DLT are like magic agreements. They self-execute when terms are met. This allows deals without needing anyone to check.
Types of distributed ledgers can vary. They might change in how they update or who gets to join. Consensus mechanisms in DLT decide how all copies agree. They make sure everyone plays fair.
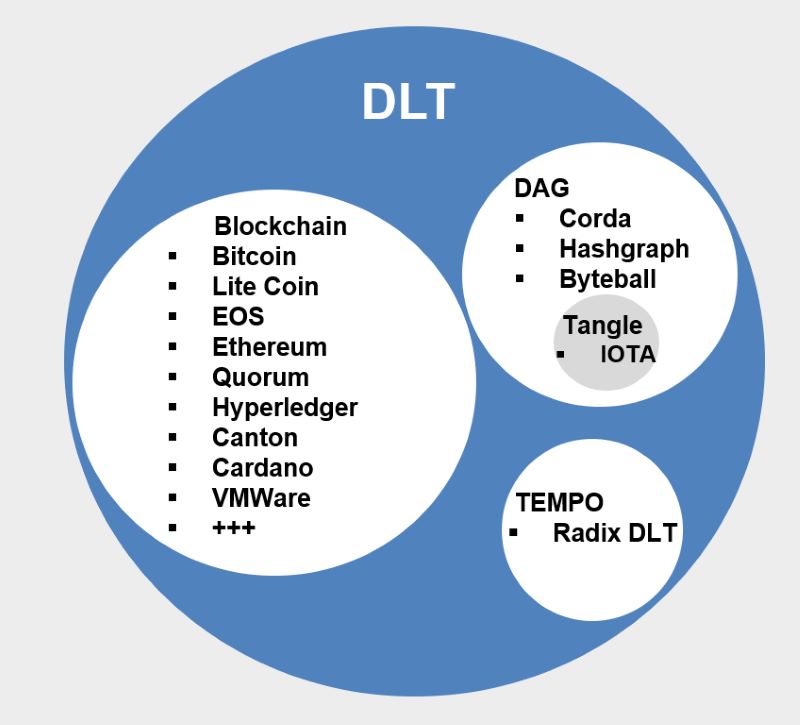
Blockchain technology is a type of DLT, known for powering Bitcoin. But it’s not the only kid on the block. There are other forms of DLT, too, each with unique features.
DLT shines in supply chain management. It tracks goods from start to end. You can see where your apple or tablet came from, all thanks to DLT.
The DLT transaction process is noteworthy. Let’s say I send you a digital coin. The DLT checks I have it to give and updates once it’s yours. It’s like a ledger that’s always up-to-date, showing who owns what.
DLT use cases are growing every day. They range from finance to voting systems to digital IDs. This tech is remaking how we do business.
Blockchain and DLT differences are key. Not every DLT is a blockchain, but every blockchain is a DLT. Blockchains are just one way to do this ledger thing. But all aim for a shared, honest view of data.
The impact of DLT on business is huge. It cuts costs by cutting out middlemen. It keeps records safe and sound. It makes businesses run smooth.
DLT for record-keeping is like a fort for your data. Hard to break in, it keeps records safe and true.
The evolution of DLT is fast. It’s always getting better, smarter, and more used. As we come to grips with DLT, we’re only just starting to unlock its full value.
Differentiating Between DLT and Blockchain
Blockchain vs DLT: Clearing the Confusion
Many people mix up blockchain and DLT. They’re close, but not the same. Blockchain is a type of DLT. Think of DLT as the main dish, and blockchain as a flavorful ingredient. All blockchains are DLTs, but not all DLTs are blockchains. DLT is the bigger picture, where blockchain fits. It’s like having a sports team, and blockchain is just one player.
Blockchain stands out for its blocks of data linked together. Other DLTs might not stack data like that. Each DLT has its own way of sharing info without giving up control. The main goal stays the same: share data fast and safe without a middle-man.
Types of Distributed Ledgers and Their Unique Characteristics
DLT is not just one thing. There are different kinds. Some use blocks of data, while others have new ways to connect info. Let’s dive into some popular types.
First, there are blockchains, like Bitcoin and Ethereum. These use blocks to store data, making a chain. They’re great for money stuff, and now, even smart contracts. Smart contracts self-execute deals on the ledger based on rules everyone agrees on. They’re neat because they cut out the need for middlemen.
Next, we have Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG). These ledgers let different parts of the data talk directly. It’s less about blocks and more about a web of connections. This can make things faster and cheaper. IOTA uses this kind for Internet of Things devices.
Then there’s Ripple. It deals with money transfers around the world. It’s a DLT focusing on transactions more than data storage. It links banks to make moving money easy and quick.
Now, let’s talk about Hyperledger. It’s like a toolbox for DLT systems. Big businesses use it to customize their own DLT. It helps with keeping records, supply chains, and identity management.
All these types use a process to agree on what’s true, called consensus. This is how they update the ledger without messing up the trust. Some use Proof of Work, like in mining Bitcoin. Others use Proof of Stake or voting systems.
Every type of DLT has a job. Some are for fast payments, others are for tracking goods or making sure contracts do their thing. Their features fit what they need to do.
DLT is changing how we think about sharing data. It’s used in fintech for secure money stuff. It tracks goods in supply chains. It even keeps records safe and straight.
These systems bring loads of perks. They make things transparent, so everyone can see what’s going on. They help keep data true and hard to mess with. This boosts trust and cuts costs.
But, there are challenges. They need to handle loads of data without slowing down or getting too pricey. This is something many are working on right now.
In simple terms, DLT is a game-changer. It’s all about spreading out control and trust across a network. Different types shine in different spots. But they all share a common theme: they get rid of the middleman and make data sharing safe and smooth.
The Role of DLT in Enhancing Business Operations
DLT Applications in Various Industries
Let’s dive right into how DLT helps businesses across the board. Think of DLT as a team where everyone keeps notes. If someone makes a change, everyone updates their notes. Now, imagine that in various industries. In finance, DLT can cut fraud and errors. Banks can see funds move in real-time. They can avoid the same money promised twice.
In health care, patient records are safe and easy to share. Doctors anywhere can pull your history fast, without mixing up details. Less waiting for you, more care time. Supply chains also love DLT. They can see where goods are, avoiding lost or fake items. Everyone in the chain knows the steps a product took to get to them.
Improving Data Integrity and Efficiency with DLT
Data integrity is a big deal today. With DLT, data is checked across the whole network. It’s hard for someone to change things without others knowing. This builds trust.
Efficiency is another win. DLT takes out middle steps in processes. Money can move faster without waiting for banks to say ok. Records update in real-time, not at day’s end. This means people can make choices quicker, with fresh info.
DLT brings clear benefits – honesty, speed, and reduced cheating. It helps businesses run smoother. But, remember, like any new tech, DLT has bits to iron out. We’ll keep working to make it better.
Future Trends and Challenges in DLT Integration
Overcoming Scalability Concerns in Distributed Ledger Systems
Scalability is a big word for making things bigger or handling more work. In DLT systems, it means letting more people use it at the same time without slowing down. Sometimes, DLT finds it hard to deal with lots of transactions fast. This is like when lots of cars hit the road at the same time and cause a traffic jam. We are working hard to fix this, so DLT can handle lots of users without a hitch.
Some smart folks are coming up with new ideas so more people can make transactions on DLT systems faster than ever. We know as more people and companies start to use DLT, it needs to be ready for action. My job is to make these systems grow big, strong, and fast. Think of it like tuning up a car so it can zoom down the track super-fast without any problems.
New tech stuff is also helping out. Things like lightning-fast networks or special ways to group transactions make DLT quicker. We call these “Layer 2 solutions,” and they’re like building a fast-moving train above the trafficky roads. This is one way we are making sure DLT can handle the hustle and bustle of today’s world.
Innovations and Evolving Use Cases for DLT
DLT is not just about coin money like Bitcoin. It’s like a super tool that can do a lot of different jobs. For example, in supply chain, DLT can make sure your stuff is checked all along its journey. From the farm to your plate, we can track your food, so you know it’s all good.
But DLT’s job is changing – it’s now in art, voting, and even in games. Artists can sell their digital art so no one can copy it. In voting, it helps make sure everyone’s vote is counted right. When you play games, it can make sure that the rare sword you got is really rare.
We also use smart contracts on DLT – these are like deals that happen all by themselves if the rules are met. This means you can trust that things will get done without someone watching over it the whole time. It’s all very cool and we’re finding new ways to use it every day.
Another new thing is how we’re fixing and upgrading these systems to do more. People are making new DLT platforms, which are like building new playgrounds with different rules and games. Each one is made for different kinds of work. This helps make sure we can use the right tool for the job.
So from buying your morning coffee with digital cash to making sure your vote counts in elections, DLT is changing the game. It’s like a big puzzle box of tech that we’re just starting to open. With every piece we fit together, we get to see a new picture of what our world could look like. And I can’t wait to see what picture we find next!
In this post, we explored the nuts and bolts of Distributed Ledger Technology, or DLT. We cleared up how it’s not just blockchain—it’s more. We looked at DLT’s unique types and what sets each apart. This tech can truly change how businesses work, making data safe and sharing smooth.
As we dove deeper, we saw DLT’s power to improve how we handle info across all sorts of fields. It’s not just talk; it’s happening now, and it’s big. Yet, it’s not all easy going. There are hurdles, like making DLT fit for more people to use. But with smart minds tackling these issues, the way we use DLT is only getting wider and wilder.
To wrap it up, DLT is a big deal. It’s reshaping our digital world, making things safer and more reliable. And that’s something to watch. Keep an eye on this space; it’s moving fast and changing the game.
Q&A :
What is DLT in the context of blockchain technology?
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) refers to a digital system for recording transactions of assets in which the transactions and their details are recorded in multiple places at the same time. Unlike traditional databases, DLT has no central data store or administration functionality. In a blockchain, which is a type of DLT, the data is stored in a sequence of blocks that are linked and secured using cryptography.
How does DLT differ from traditional databases?
Unlike traditional databases, DLT is decentralized and records information across a wide range of networks. There is no single point of control or failure, which can increase security and reduce vulnerability to fraudulent activities. Each participant in a DLT network has a copy of the ledger for full transparency and shared verification of transactions.
What are the advantages of using DLT in blockchain?
The use of Distributed Ledger Technology in blockchain offers numerous advantages including improved security and integrity of data due to its immutability. It also enhances transparency and trust as all participants have access to the transaction history. Additionally, it removes the need for a central authority, potentially reducing costs and increasing the speed of transactions.
Can DLT be applied to industries outside of finance?
Yes, DLT can be applied to a wide range of industries beyond finance, including healthcare for patient data management, supply chain for real-time tracking of goods, real estate for land registry, and more. Its ability to provide a secure and transparent ledger of transactions makes it versatile for various applications that require accurate and immutable records.
What are the potential challenges of implementing DLT?
The implementation of DLT can pose certain challenges, such as scalability issues, as the number of transactions increases on a network. There might also be legal and regulatory concerns, as the technology is still evolving and jurisdictions may have differing approaches to its use. Furthermore, the required consensus among participants on a distributed ledger could lead to slower transaction times compared to centralized databases.