Consensus Algorithms Unveiled: Navigating the Backbone of Blockchain Technology
Dive deep into the tech that keeps crypto ticking: what is Consensus Algorithms? Picture a room where everyone’s voice counts. In the world of blockchain, this ‘room’ is huge, and the ‘voices’ are computers talking to keep money safe and transactions clear. It’s a system where trust isn’t just asked for; it’s built, block by block. Join me as we unveil the craft behind this key player. With every click, learn how these silent digital negotiators shape the DNA of blockchain, ensuring everyone agrees without a shadow of a doubt that the deal is fair. This is where secure meets savvy – let’s break it down together.
Understanding Blockchain Consensus Algorithms
Defining Distributed Ledger Technology
Imagine a book that keeps track of every trade in a market. This book is open to anyone. A playground game of tag has simple rules, right? Picture if you had to agree on who’s ‘it’ using those same rules. That’s like a blockchain. Each block in a blockchain is a new page in our book, showing trades made. Everyone sees it, so everyone knows the score.
The Role of Consensus in Cryptocurrency Governance
Consensus is finding common ground in choices, even when folks disagree. In the crypto world, it’s like agreeing on the game rules before we start. Mostly, it means making sure everyone’s copy of the blockchain, our big book of trades, is the same. This stops cheats and keeps the game fair.
In the land of bits and coins, a group called validators play a vital part. They’re like referees, checking each trade to keep the game clean. Now, there are different ways these refs can agree on what’s a good trade and what’s not. They use rules called consensus mechanisms. This is big brain stuff, ensuring no one breaks the trade book’s rules.
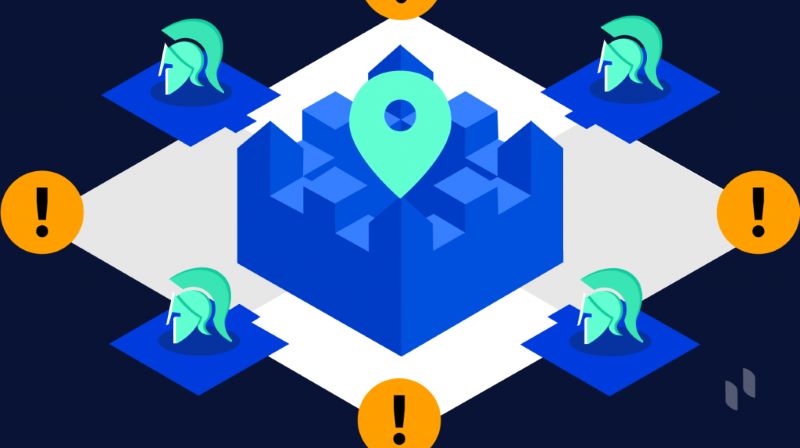

When we talk about these rules, things like Proof of Work and Proof of Stake pop up. They’re just types of consensus mechanisms, rules of the game that validators must play by. Proof of Work makes validators solve tough puzzles to prove they’re serious. It’s hard and uses lots of energy. Proof of Stake is a bit friendlier on the power bill, making validators chip in money as a promise to play fair.
Understanding blockchain consensus is like getting why we need rules in our tag game. Without them, it’ll just be chaos, and no one would ever agree on who’s ‘it.’
They say Byzantine Fault Tolerance is like having a plan if one of us starts cheating. It’s about keeping the game going, even when things get messy. Blockchain validation is a lot like using this plan to stop the cheaters so we can keep trading games fair and square.
In the land of the cryptos, keeping the ledger as tight as a drum is king. The role of consensus in crypto is pretty much everything. Without it, we can’t trust the book, and without trust, we’ve got nothing.
Games need rules and a fair ref. Same for trade books in crypto land. Consensus makes sure the game’s fair, the book’s right, and the trade’s tight. With it, crypto stays safe, fair, and keeps on trucking like a champ.
Comparing Proof of Work versus Proof of Stake
Advantages and Limitations of PoW
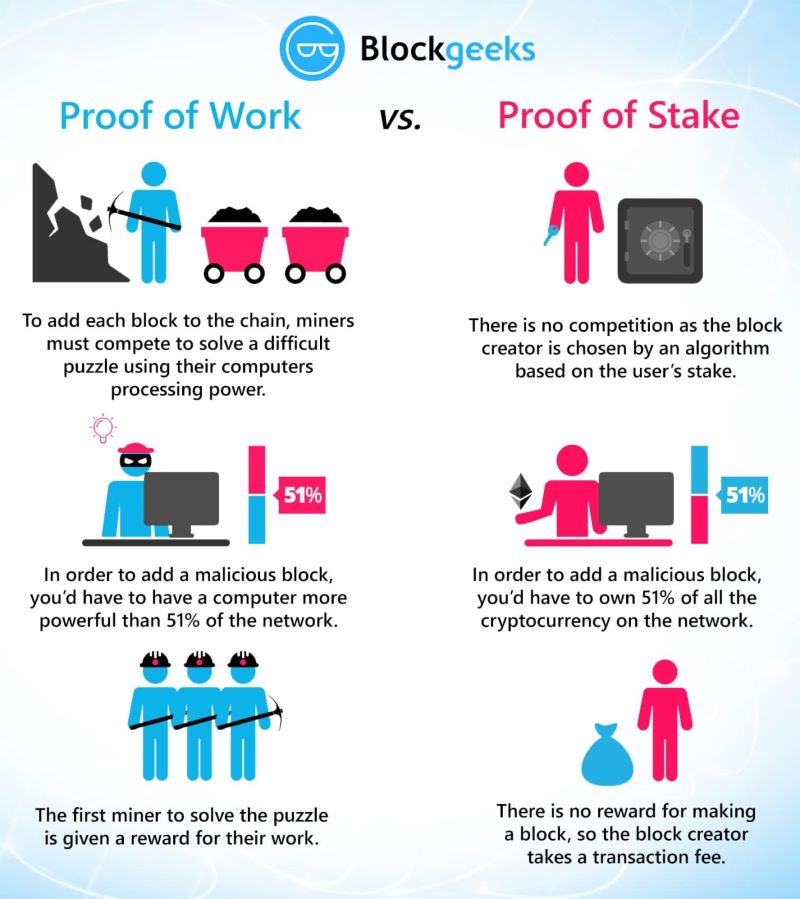
Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) are like the heart of blockchain. They help everyone agree on the records. PoW keeps the network safe by making people solve hard math problems. But, it uses lots of energy, like turning on a whole country just for math.
Now, let’s get why PoW is a hot topic. It was the first pick for Bitcoin. It is secure because it is hard to trick. It stops double spending, where someone spends money twice. But it has a huge problem: it eats up more energy than many countries.
PoS as a Solution for Algorithm Efficiency and Energy Consumption
Enter Proof of Stake (PoS). Think of it as a greener friend. It uses less juice, and it’s like having a raffle. The more coins you hold, the better your chances to add new blocks to the chain. It’s like holding a lot of tickets in a big raffle.
PoS makes people “stake” their coins as a promise they are honest. If they try to cheat, they lose their coins. This way, the system needs less power to work. It is like having a guard who uses brain over brawn.
Many love PoS because it is light on the power bill. It also lets more people join in without needing big, expensive computers. This makes it better for our planet and it opens doors for more folks to play a part in blockchain.
So, to sum it up, PoW is like an old, trusty truck – strong but thirsty for fuel. PoS, on the other hand, is like a smart car, easier on the environment and nifty. But both are key in helping keep our digital money safe and sound.
Exploring Advanced Consensus Mechanisms
Byzantine Fault Tolerance and its Variants
Think of Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) like a tough guard. It protects a system even if some parts fail or act bad. It’s key to keeping data safe and sound in blockchain. With BFT, even when things mess up or someone tries to trick the system, it still works right. This guard doesn’t stand alone. It has buddies like Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), which is like a smart version that saves energy and time when making sure everything’s running smooth.
From Nakamoto to Delegated Proof of Stake: The Evolution of Consensus
Let’s dive into the ocean of consensus mechanisms, swimming from Nakamoto consensus to Delegated Proof of Stake. We started with Nakamoto, the simple, strong base supporting Bitcoin. Its main tool, mining, helps keeps the network secure and updates the blockchain. But mining takes much power, like a huge, hungry machine. So, the journey continued.
Proof of Stake came next. It said, “Why not just use owning coins as power to validate?” It’s like having a club card that gives you the chance to update the ledger and earn some rewards. No more heavy machines; just coins in your pocket.
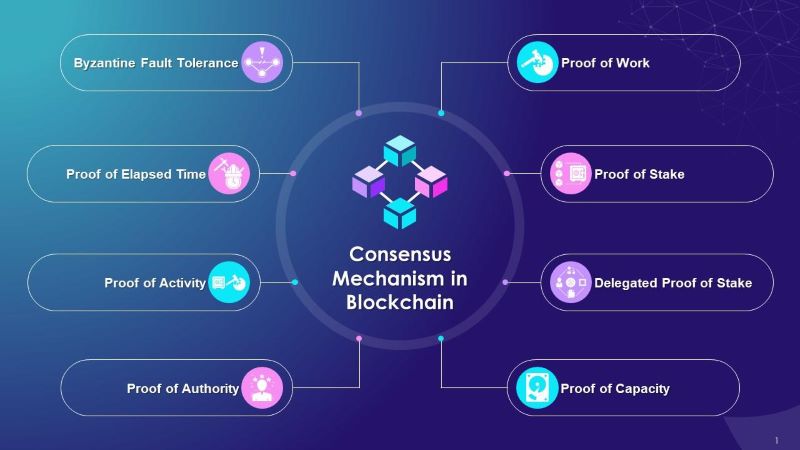
Then, the Delegated Proof of Stake stepped in and refined things. It works like electing a group of class reps who can speak and act for everyone in the system. They help the blockchain use less power and run fast. This method helps a lot when more people join in and the network grows bigger.
As we look into these mechanisms, we understand why they’re so important. They are the engines that keep the blockchain car running. With no engine, no go. Each one plays a role, from keeping our crypto buys safe to making sure smart contracts do what they should.
By knowing these engines, we get a better sense of how blockchains stay secure. We see how they adapt and change to fit the needs of growing, buzzing networks of people all over the world. From simple beginnings to smart, sharp systems, the journey of consensus shows a path of non-stop growth and better ideas shaping our digital world.
The Future of Blockchain Validation Processes
Addressing Scalability through Consensus Models
In blockchains, we all want things to be fast and smooth. We have a problem called scalability. It’s like wanting more cars on a road without causing a big jam. To fix this, we use special rules called consensus models. They’re like traffic lights on the internet. They help lots of transactions happen without crashing the system.
One main model is Proof of Work. It’s a bit slow because it uses a lot of computer work to add new info to the blockchain. It’s like solving a hard math problem before you can put your car on the road.
Then there’s Proof of Stake. It’s faster because instead of math problems, it uses a system where people lock up some of their crypto money as a promise they’ll follow the rules.
There are other models too, like delegated Proof of Stake. Here, people vote for a few to do the hard work for everyone. It’s like choosing a driver to navigate through traffic for you.
These models work hard to let more transactions happen at once. They make sure everyone follows the rules so everything runs well.
Enhancing Blockchain Security: Validator Nodes and Sybil Attack Prevention
Now, let’s talk security. It’s super important for a blockchain to be safe. We have these things called validator nodes. Think of them as guards that check transactions to keep them honest. They work hard to spot the bad guys.
There’s this tricky problem named the Sybil attack. It’s when one person pretends to be many to trick the blockchain. But our guards, the validator nodes, use their special ways to stop this. They check if each user is real and follows the rules.
The whole point is to keep our crypto safe and the blockchain trustworthy. It’s like making sure no one sneaks onto the bus without a ticket. By using the right consensus models and validator nodes, we keep everything secure and running smooth. It’s work, but it’s worth it. We all get to enjoy a blockchain that’s fast and safe.
In this post, we dug into how blockchains make sure everyone agrees on the records. At first, we defined what distributed ledger tech is and why consensus matters in managing digital coins. Then, we compared Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), covering their pros and cons. We noted that PoS steps up as a fix for PoW’s heavy energy use.
Next, we explored complex ways of reaching agreement like Byzantine Fault Tolerance. We saw how these systems have grown from Satoshi Nakamoto’s first ideas to what we have today with Delegated Proof of Stake.
Looking ahead, we talked about how blockchains can handle more users and secure their records better. In the end, getting consensus right means a faster, safer system for everyone. This topic’s deep, so stay curious and keep learning. Blockchains are shaping our future, and understanding how they work is crucial. Keep your eyes on how consensus models evolve. They’re the key to a secure and smooth digital world.
Q&A :
What Are Consensus Algorithms and How Do They Work?
Consensus algorithms are a fundamental component of blockchain technology and distributed ledger systems. They ensure that all participants in the network agree on a single source of truth, even in the absence of trust among parties. Essentially, they provide a way to achieve reliability in a network involving multiple nodes. By using consensus algorithms, decentralized networks can make decisions and validate transactions without a central authority.
Why Are Consensus Algorithms Important in Blockchain?
In blockchain technology, consensus algorithms play a critical role by enabling the network to agree on the state of the ledger securely and efficiently. They prevent double-spending and ensure that the integrity and the order of transactions are maintained. Without consensus algorithms, any distributed network would struggle to confirm the authenticity and chronological order of transactions, making blockchain technologies like cryptocurrencies and smart contracts inoperable.
What Types of Consensus Algorithms Exist?
There are several types of consensus algorithms used in various blockchain networks, including Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), among others. Each one has different mechanisms, advantages, and drawbacks concerning security, energy consumption, scalability, and speed, which makes them suitable for different kinds of networks and applications.
How Does a Consensus Algorithm Ensure Security?
A consensus algorithm ensures security by establishing rules and a process by which all the nodes in the network agree on a shared ledger’s content. This process includes validating transactions and blocks, following a specific protocol to resolve any conflicts, and protecting against fraudulent activities and malicious actors who may try to compromise the network. By requiring a mathematical proof or a majority vote before making any changes to the ledger, consensus algorithms help maintain a secure and tamper-resistant system.
Can Consensus Algorithms Fail, and What Happens If They Do?
Consensus algorithms can fail or encounter issues if there’s a significant number of malicious nodes in the network, if there are flaws in the algorithm design, or due to unforeseen technical problems. If a consensus algorithm fails, it can lead to forks in the blockchain, double-spending, or a complete breakdown of the network’s trust. This is why the design and the testing of consensus algorithms are critical for maintaining the resilience and reliability of a blockchain system.