Comparative DAG vs Blockchain: tech moves fast, and so should we. I’ve seen the changes first-hand. The future of tech mastery lies here, but it’s a tangled web to unweave. We’ve got two giants: DAG with its web-like paths, and Blockchain with its sturdy blocks. They both carry our digital world, but in their own ways. Understanding their strengths and weaknesses could change the game for us all. So, let’s dive right in. Together, we’ll explore the brass tacks of these technologies, assess their speeds, and their punch in the real world. We’ll weigh their energy hunger and sift through their challenges. Get ready to make sense of two tech titans vying to shape our digital destiny.
Understanding the Basics: DAG and Blockchain Explained
Defining Directed Acyclic Graph Technology and Its Operation
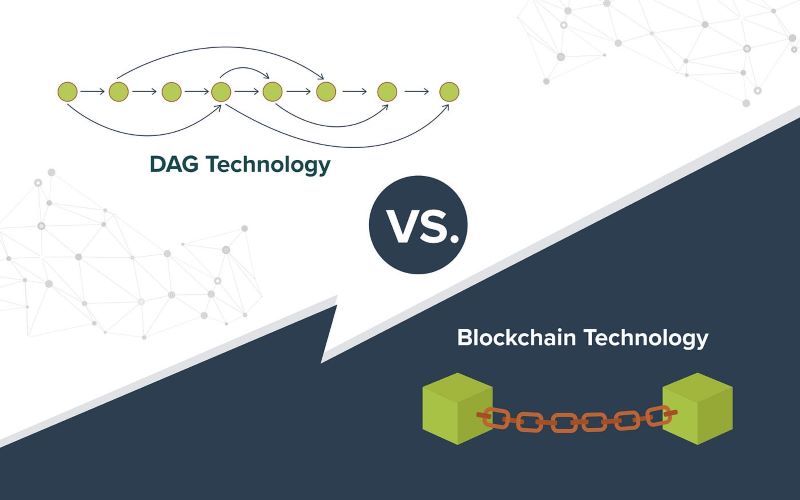
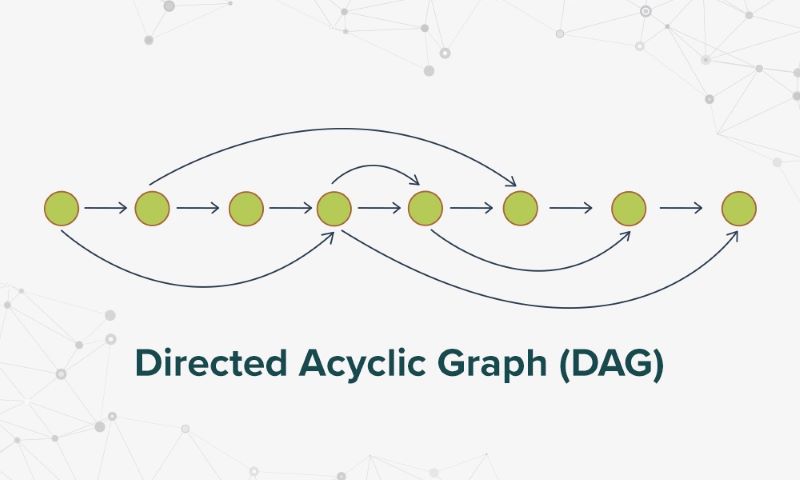
What is a Directed Acyclic Graph in tech terms? A Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a network of items. They point from one to another in one direction, and they never loop back.
Imagine a team game where a ball moves from player to player but can never pass back to someone who has had it before. That’s how DAGs work with data. Nodes (the players) pass on transactions (the ball) forward along the graph. There’s no going back or creating circles. This makes DAGs different from other systems. DAG technology shines in its speed and the ability to handle lots of data at once, or what we call scalability. Think of it as the quick, nimble player that does well when the game speeds up.
DAGs have a big role in making cryptocurrencies work better. They are behind some fresh and energy-saving options like IOTA’s Tangle. This network connects devices in the Internet of Things (IoT), making it easier for machines to talk to each other.
The Fundamentals of Blockchain Structure and Mechanisms
So, how does a blockchain structure stand up next to DAG? Think of Blockchain as a chain of digital blocks, each holding bunches of transactions. A new block is like adding another link to the chain.
Blockchain is like an assembly line. It adds one new part at a time to make the final product. It’s careful, making sure everything checks out before moving on. These checks are done through mining, a tough puzzle-solving task that keeps the chain secure.
Proof of Work is the main way blockchains stay safe. It makes sure that all who join in do the work and back up their moves with computing power, much like putting a ticket into a drawing for every hour you work. The more you work, the more likely you’ll get to add a block to the chain.
A benefit of blockchain is that once data is added, it’s very hard to change, which means it’s reliable. But this firm setup can be slow. It often creates traffic when many users join in, like a crowded road during rush hour.
DAG is different. It’s built to grow without slowing down, which can make it better when the pressure is on. Without the need for mining, it slashes costs and energy use, making it a friendlier choice for our planet.
Comparing Blockchain and DAG is not about picking a winner. It’s about finding the right tool for the job. They’re both types of distributed ledgers but solve different problems. Where Blockchain is like a train—powerful and secure—DAG is like a fleet of bikes: swift, flexible, and green.
As we connect more devices online and grow our thirst for quick, open tech, it’s clear DAG has plenty to offer. But with Blockchain’s strength in security, it’s still the go-to for many who need strong, lasting transaction records.
In this tech race, as in most, being smart about which horse you bet on counts more than just picking the fastest. It’s about matching tech powers to our real-world needs, and in that, both DAG and Blockchain have the muscle to carry us into a future full of promise.
Analyzing Performance: Transaction Speed and Scalability
Speed of Transactions in DAG and Their Impact on Real-World Applications
DAG is a champ when we talk speed in tech. This tech shines in real-world use. Think of being in a store, and you tap your phone to pay. With DAG, that payment zips through, quick and easy. In a DAG system, each person who makes a transaction helps confirm others’ transactions too. So, more action on the network means things move faster. This teamwork makes the dream work.
This speed is why IoT loves DAG. It’s great for handling loads of tiny data exchanges between devices, fast! Each device talks to the next, no need to wait for approval from far off. With IoT growing fast, DAG fits like a glove. Making our smart world smarter and smoother.
Confronting Blockchain Scalability Issues and Confirmation Times
Now let’s peek at Blockchain. It’s the big name; everyone knows it. It started the crypto buzz after all. But here’s the hitch: as it gets popular, it slows down. Imagine a single road getting busier. Traffic jams, right? That’s a bit like Blockchain when too many people use it at once.
With Blockchain, miners play a game to verify stuff. Winners add a new block and get crypto coins. But this takes time. Sometimes, it’s minutes. Other days, it’s hours. This waiting game is called ‘confirmation time’. It’s a pain when you’re in a hurry.
Blockchain’s a tough nut to crack. Folks are trying though. They’re building new ways to make it scale. But it’s a tall order, trying to keep it safe and speedy at the same time. And that’s where DAG has a sneaky lead. No miners, no race, just fast tracks.
Both DAG and Blockchain are hot stuff in tech. They’re like different flavors of ice cream. One’s quick and zesty – perfect for quick nips and tucks in tech. The other’s more like a rich, classic choice, solid and trusted. They’ve both got their perks. They’ve both got their quirks.
In the race of tech, think of DAG like a sprinter. It’s out the gate and down the track in a heartbeat. Blockchain’s more the strong, silent type. A marathon runner with lessons to teach us about staying power. But both have their eyes on the prize – shaping a future that’s smart, safe, and speedy.
Examining Consensus and Energy Consumption
Evolution of Consensus Mechanisms in DAG vs. Proof of Work in Blockchain
Let’s talk about how computers agree on things. In the crypto world, they need to agree on who has what. It’s like having umpires in a game. But how they decide can be pretty different.
How do DAGs decide who has what?
Fast and together. In DAGs, every user helps to check transactions. It’s like each player helping to call the shots. This way, it’s quicker, and everyone’s in the loop. Examples, like IOTA’s Tangle, show this in action.
DAG technology lets lots of transactions happen at once. That means things can move fast, real fast. No waiting in line, no taking turns. It’s a free-for-all, but in a good way. Each new bit of info helps confirm the old stuff.
How does Proof of Work decide in Blockchain?
It takes its time and makes sure. Computers called miners work hard solving puzzles. It’s a race to see who can do it first. The winner tells everyone what’s what and adds a new block to the chain.
This method is kind of slow. It also takes a lot of power.
Scaling the Environmental Impact: Blockchain Energy Consumption vs. Energy-Efficient Cryptocurrencies
Now, let’s chat about power – the electric kind.
How much energy does mining in Blockchain use?
A whole lot. It’s like having all the lights on non-stop in a big city. Every miner across the globe is trying to solve those puzzles. And just one can use as much power as a whole house.
But it’s not just about the lights. Big energy use means more carbon footprint. With everyone talking about saving our planet, this is a big issue.
What are energy-efficient cryptocurrencies?
A breath of fresh air. These are the new kids on the block. They don’t need miners playing guessing games. Instead, they use less power to agree on things. It means less stress on our world. DAGs shine here because they’re designed to sip power, not gulp it.
They’re like electric cars compared to gas guzzlers. And in a world that’s going green, that’s a great thing. We’re talking about fewer fumes and a happier planet.
So, when we look at these, we see big differences. DAGs are like a group project — working together for the win. Blockchains? More like a solo race with a power-hungry engine.
It’s clear consensus and energy are huge deals in figuring out the tech future. It’s about finding the best way for us all to agree without making Mother Earth pay the price.
Advancements and Challenges in Implementation
The Integration of Smart Contracts: Comparing Blockchain and DAG Platforms
Smart contracts are like magic spellbooks. They make deals happen with no human fuss. On Blockchain, they run on a system you’ve heard of: it’s called Ethereum. To kick off a smart contract here, you pay a fee. Each action within this digital contract fuels the Blockchain. These fees can add up, making some folks think twice.
DAG platforms switch it up. They let these contracts run with little to no costs. Take the IOTA Tangle, for example. No miners, no fees, and its Tangle web makes it work. That means we can set up smart contracts cheaper and faster. Things look good for businesses and coders who need speed and savings.
Transaction Finality and Security: Blockchain vs. DAG in Cybersecurity and Finance
Now, let’s talk about keeping things safe and making sure a deal’s a deal. In the Blockchain world, once a block sticks, it’s like carved in stone. With Bitcoin, it takes a bit, but after about an hour, you can rest easy. The catch is, sometimes forks happen. A fork is like a road splitting. Two paths, but only one can win. This makes folks nervous, but don’t worry, it’s rare.
DAG’s different. No blocks here, just lines zipping from one spot to another. This web makes it hard to double spend, which is cheater talk for spending twice. With DAG, once the network agrees, it’s locked in. Final. No going back, no forks, no sweat.
In the finance and cybersecurity game, that’s big news. Banks and pros like it for keeping money safe. They trust DAG to seal the deal quick and keep hackers away. With tech like this, we can see a future with smooth and secure money moves.
We’ve covered the nuts and bolts of DAG and blockchain, laying out their key features and how they differ. We dug into transaction speeds, noting DAG’s edge in real-world tasks, and addressed why blockchains struggle to grow without a hitch. Our talk on consensus touched on DAG’s newer methods versus blockchain’s energy-heavy Proof of Work. Plus, we looked at how both techs tackle smart contracts, security, and their role in finance.
In short, DAG shines with speedy transactions and energy savings, while blockchain stands firm on its proven security. Yet, both face challenges in wider use. They’re changing the game, for sure. Keep an eye out; this tech is moving fast!
Q&A :
What are the main differences between a DAG and a blockchain?
DAG, which stands for Directed Acyclic Graph, is a data structure that allows for multiple chains of blocks to interweave with each other, enabling higher scalability and potentially lower transaction fees due to parallel processing. Blockchains, on the other hand, are a single chain of blocks where each block is connected to the one before it, forming a linear sequence. This often results in slower transaction speeds and higher costs compared to DAGs, especially when the network is congested.
How does a DAG improve upon traditional blockchain technology?
DAG technology improves upon traditional blockchain by offering a more scalable solution. In a DAG, transactions can be processed simultaneously, rather than having to wait for previous transactions to be added to the chain. This can lead to much faster confirmation times. Additionally, because of the reduced need for miners or validators to confirm transactions sequentially, the overall energy consumption can be lower for DAGs than traditional blockchains.
Is the security of a Comparative DAG equivalent to that of blockchain?
The security of a DAG can be different from that of traditional blockchain technology. While blockchain relies on the security provided by the chain of cryptographic hashes, DAGs must implement alternative security measures due to their non-linear structure. These measures may include selecting reputable nodes for transaction validation or employing other cryptographic techniques. The security of a DAG largely depends on its architecture and the consensus mechanism it uses.
Can you use smart contracts on a DAG network?
Whether smart contracts can be used on a DAG network depends on the specific DAG’s capabilities. Some DAG networks are designed to support smart contracts, enabling decentralized applications to be built on top of them, just like on blockchain platforms. However, not all DAGs have this functionality, so it is important to investigate the features of the specific DAG network in question.
What are the potential use cases for DAG technology over blockchain?
DAG technology is particularly well-suited for applications that require high transaction throughput, microtransactions, or IoT (Internet of Things) deployments. Use cases include payment systems that need to operate at a large scale with minimal fees, supply chain management where numerous small transactions occur frequently, and managing data from a multitude of sensors in a network. DAG’s ability to process transactions in parallel makes it ideal for these scenarios, where the linear approach of blockchain might be a limiting factor.


