What is distributed ledger technology in blockchain? It’s the backbone changing how we handle data. Imagine a world where every transaction, every exchange of value, and every agreement happened with total trust and transparency. That’s the reality Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is crafting, a fresh system for exchanging and securing digital information. It’s not just tech talk—it’s the future, right in front of us. Stick with me, and let’s unravel this tech tangle together. From its essence to its role in our digital world, you’re about to become the person in the room who explains it with ease. Buckle up for a ride into the ledger that’s everywhere, yet belongs to no one.
Demystifying Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
The Essence of DLT Fundamentals
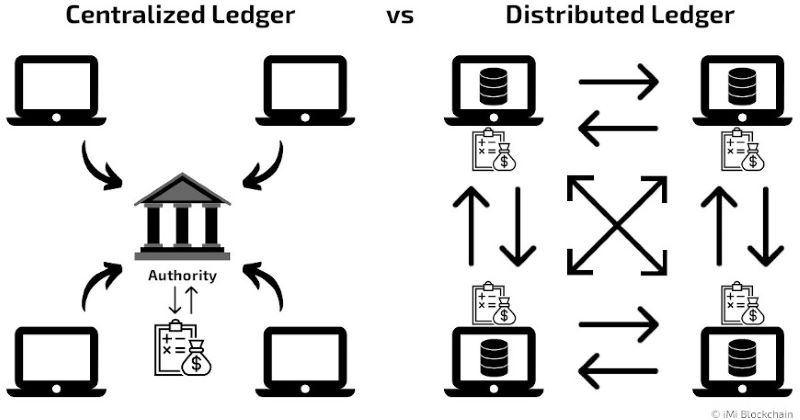
So, what’s this buzz about Distributed Ledger Technology, or DLT? In simple terms, DLT is like a digital ledger that’s not kept in one place. Instead, it’s spread out across many computers. These computers can be across the room or around the world. They all hold copies of the same ledger. Imagine a book where all the copies have the same stories. If one book changes, they all do, so the story stays true.
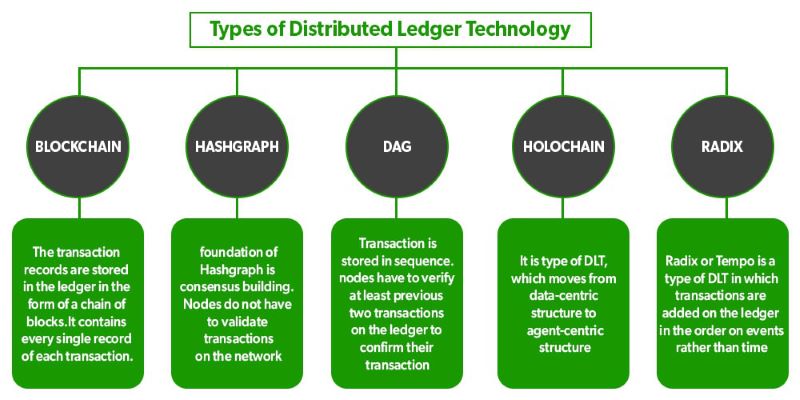
These ledgers are digital, tracking stuff like money, goods, or property. Each entry is like a promise that something happened, a bit like saying, “I owe you,” but super secure. This tech powers blockchains, but not all DLTs are blockchains. A blockchain is a type of DLT, one with data stuck together in “blocks.”
Core Components of DLT Systems
Now, let’s dive into the parts that make up DLT systems. First thing’s a network of computers – we call them nodes. Nodes are like little helpers. They all keep a copy of the ledger and check in with each other to stay updated. They agree on what the ledger says using rules, or a consensus mechanism. This is how they ensure all copies are the same, without needing a boss to check their work. These rules vary and are super important for trust.
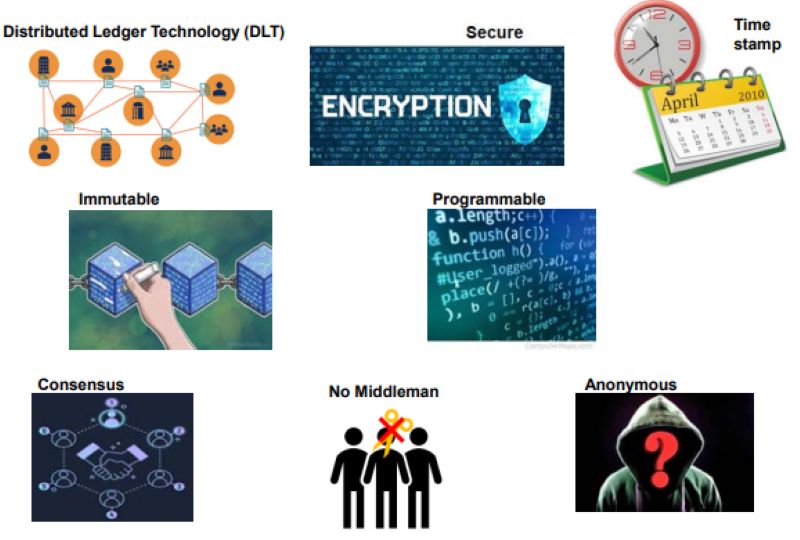
Next up, we have the ledger database. This is where all the info gets stored. It’s like a library of everything that’s happened in the network. It’s super tough to change old data here, which is why we say DLT is immutable. This means once something is written, it’s nearly impossible to change. That’s great for trust too.
Another big part is cryptographic security. It’s a fancy way of locking the data with math so only the right people can see or change it. Think of it as a secret code that keeps your stuff safe from the bad guys.
Lastly, DLTs can be public or private, meaning who gets to participate. Public ledgers let anyone join in and help out. Private ledgers only let certain people in, like a VIP club.
So, DLTs are like shared ledgers, secure and tough to change, where everybody follows the same rules to keep things fair and square. They can help us track and trade nearly anything without worrying that someone’s messing with the records. From money to music, if it can be listed, a DLT can probably handle it. And that’s pretty cool, right?
Understanding Blockchain and DLT Interplay
Clarifying the Blockchain vs. Distributed Ledger Confusion
Think of blockchain as a type of distributed ledger. Not all ledgers are blockchains, but every blockchain is a ledger. Most people mix them up. But once you know the difference, it’s clear as day.
Blockchain is special because it chains data together. In other types of ledgers, the data isn’t chained. They all share info across many places though. This means they are safe from losing data if one spot fails. It’s like having many copies of a photo. If you lose one, you’ve got backups.
Various Types of Distributed Ledger Systems
Now let’s talk about the different kinds of ledgers. You’ve got public ones that anyone can see and use, just like a park open to all. Then there are private ones, where you need an invite, like a backyard BBQ.
Some ledgers need permission, and some don’t. Permissionless ledgers let anyone join in. They can send out info or help keep the ledger updated. Permissioned ones are tighter. They pick who can help out. It’s like having a list for who can come into a club.
Ledger databases in the blockchain are where all the info stays. It’s neat and organized. This helps everyone agree on what’s true, without needing a boss. It’s like a group project, but everyone sees every part of the work.
In these systems, there are rules for agreeing, called consensus mechanisms. They make sure everyone plays fair. Then there’s the data structure in DLT. It’s how info gets stored and how complex it is.
A super important part is the peer-to-peer network in DLT. It connects folks directly. This way, info goes straight from one person to another. No middlemen needed. And with cryptographic security in blockchain, it’s like having secret codes for your info. Only the right person can read it.
There’s a lot of talk about public versus private ledgers. Public ones let us see everything, which is great for trust. But private ones keep things under wraps. This can be key for businesses that need to keep secrets.
The beauty of DLT is in its strength. Info can’t be changed once it’s added, a feature called immutability. It’s like writing with a marker that won’t rub off.
And these systems are all over the place in business. They change how money moves in financial services. They let us use smart contracts that act on their own, when conditions are met. It’s like having a robot that makes sure a deal goes as planned.
At the core, DLT is about spreading out control and trust. It makes systems stronger and more fair for everyone. And that’s just the start. These ledgers are changing how we interact with the digital world. It’s a big shift that’s just getting going. And it touches so much: from money, to how we keep track of things, to making sure deals go right. It’s all built on trust in the ledger, and that’s pretty amazing.
The Mechanism Behind DLT’s Operation
Exploring Consensus Mechanisms in DLT
In a world where everyone wants to agree but hardly does, distributed ledger technology (DLT) is a standout. It makes people who don’t even know each other agree on what’s true digitally. This is where consensus mechanisms shine. They are the rules that keep everyone on the same page. Think of it like a game where everyone needs to play by the rules, or else the game falls apart.
Consensus mechanisms in DLT are key. They make sure all the computers in the network agree on a single truth. This is hard to do because computers are all over the world. They don’t know each other but still need to trust what they agree on. It’s a bit like having a giant group chat where everyone has to agree on what happened, even if they weren’t there.
Now, you’re likely wondering, what does a consensus mechanism do? Precisely, it makes sure new data added to the ledger is the real deal. It’s the guardian of truth in the DLT world. Without it, people could cheat, and the ledger would be a mess.
The Role of Cryptographic Security
When it comes to keeping our digital stuff safe, cryptographic security in blockchain is a big deal. It’s like having an unbreakable lock on your diary. No one but you can read your secrets. In DLT, cryptographic security keeps our digital things safe from bad folks.
Again, you might ask, how does cryptographic security work? Imagine this: every piece of data is scrambled into a secret code. This code is so hard to crack, it’s like trying to solve the world’s hardest puzzle. Even if someone got their hands on your data, they wouldn’t make heads or tails of it.
In the heart of DLT lies this uncrackable code, making sure that once something is saved, it stays as it is. It can’t be changed or deleted. It’s like carving into stone. This unchangeable nature is called immutability, and it’s a cornerstone of trust in DLT networks.
You see, trust in distributed ledger networks is about more than just believing in good faith. It’s built on this solid, unbreakable cryptographic foundation that keeps everyone’s actions in check. It also makes sure the stuff you see on the ledger is the same stuff everyone else sees. This transparency can change the way we do pretty much everything, from paying for stuff to keeping records.
In short, DLT is the wonder behind many things we’ll do in the future. It’s the silent force that keeps honesty in check in a digital world. It uses consensus mechanisms to maintain order and cryptography to keep our data locked up tight. It gives us a new way to think about how we trust what we see online.
Real-world Applications and Implications of DLT
Enhancing Efficiency: DLT in Financial Services
Picture a world where every payment is fast and safe. That’s DLT at work in banks. It cuts costs and wait times for people moving money. Understanding blockchain technology helps us see how DLT changes finance games. It’s about more than money; it can also help us keep track of who owns what, in a way everyone trusts.
Now think about how we trade. DLT lets us trade quicker by using computers to agree on trades. Everyone in the trade uses the same data, so it’s clear and fair. What makes DLT unique is how it shares data. It sends copies of a ledger to everyone in the network. This way, data is not just in one place, so it’s harder to lose or change.
But what are these ledgers? They’re like lists or records of what’s happened. Types of distributed ledger systems matter in finance. Private ledgers help keep things secret when needed. Public ones let everyone see what’s happening, which can be good for trust. Both have their uses depending on the goal.
The guts of DLT—the parts that make it work—are clever too. They use tricky math to make sure no one can mess with records. That’s cryptographic security in blockchain. And to make decisions, they use something called consensus mechanisms in DLT. That means instead of one boss, the computers work together to agree.
The Future of DLT: Integration and Expansion Possibilities
Now let’s dream a little about the future. DLT isn’t just cool for finance. It can change how we do so much more. For example, it’s top-notch for keeping records safe. Hospitals, schools, and even governments can use DLT to keep track of important info. And, because it’s tough to change old data, we know it’s true and that builds trust in distributed ledger networks.
Let’s say you want to buy music, games, or art. With DLT, artists can get paid directly, no middleman needed. That’s DLT’s peer-to-peer network and DLT at work. They let folks connect directly and make sure everything’s on the level.
What’s really exciting is how DLT can grow and fit into our lives even more. Scalability of distributed ledgers is a fancy way to say it can handle more and more folks using it. And as we use it more, DLT might help us do things we haven’t even thought of yet!
Think of DLT as the helpful teammate we all wish we had: keeping our stuff safe, making sure we all agree, and ready to grow with us. It’s no wonder we’re all trying to fit DLT into our worlds. Whether it’s switching up how banks work or finding new ways to make sure artists get their fair share, DLT looks set to stick around.
In this post, we dug into the basics of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) and how it works. We looked at what DLT is and the key parts that make it tick. Then, we cleared up how blockchain fits with DLT and checked out different kinds of DLT systems.
We also dived into how DLT systems agree on updates and the part that secret codes play in keeping it safe. To wrap up, we explored how DLT helps money services work better and thought about where DLT could go next.
I believe DLT has a huge role in shaping our future. It’s not just tech talk – it’s a game-changer for how we will interact, bank, and do business in years to come. It’s smart to keep an eye on DLT as it grows and finds new ways to make our world run smoother. That’s it, folks – DLT could be the key to an exciting, efficient future.
Q&A :
What is Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) in Blockchain?
Distributed Ledger Technology, commonly known as DLT, refers to a digital system for recording the transaction of assets in which the transactions and their details are recorded in multiple places at the same time. Unlike traditional databases, DLT has no central data store or administration functionality. Within blockchain technology, which is a type of DLT, this means that each block in the chain contains a number of transactions, and every time a new transaction occurs on the blockchain, a record of that transaction is added to the ledger of each participant. DLT is a key innovation introduced by blockchain technology which ensures security, decentralization, and consensus.
How does Distributed Ledger Technology ensure accuracy and trust?
The accuracy and trust in Distributed Ledger Technology come from its decentralized nature and the use of consensus mechanisms. Every transaction on the ledger is independently verified by a consensus process among the network’s participants, for example through methods like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake. Once a transaction is confirmed, it is encrypted and linked to the previous transaction in the blockchain, creating a secure and unalterable chain of records. The replication of the ledger across many nodes ensures that each participant has an identical copy of the ledger, increasing transparency and making it very difficult to alter any transaction retrospectively, which builds trust among the users.
What are the main advantages of using DLT in blockchain?
One of the primary advantages of using Distributed Ledger Technology in blockchain is increased security. The decentralized nature of DLT means that there is no single point of failure, making it more resistant to malicious attacks and fraud. It also ensures transparency as all participants on the network have access to the same information and any changes to the ledger are immediately visible to everyone. This encourages trust among users. Additionally, DLT can significantly reduce the time and cost associated with traditional transaction processes by eliminating the need for intermediaries and ensuring direct peer-to-peer transactions.
Are there different types of Distributed Ledger Technologies?
Yes, there are several types of Distributed Ledger Technologies available. The most well-known is blockchain, but there are others like directed acyclic graph (DAG), which is used by IOTA, and Ripple’s consensus ledger. Each of these technologies operates on the same basic principle of decentralization and distributed data, but they have different methods and architectures for achieving consensus and ensuring the security and integrity of the transactions recorded.
Who benefits from implementing Distributed Ledger Technology?
A wide range of sectors can benefit from implementing Distributed Ledger Technology. This includes, but is not limited to, finance for secure and rapid transactions, supply chain management for the traceability and verification of goods and materials, healthcare for maintaining confidential patient data, and government for improving transparency and efficiency in administrative processes. Essentially, any industry that requires secure, transparent, and immutable record-keeping can potentially benefit from DLT.


